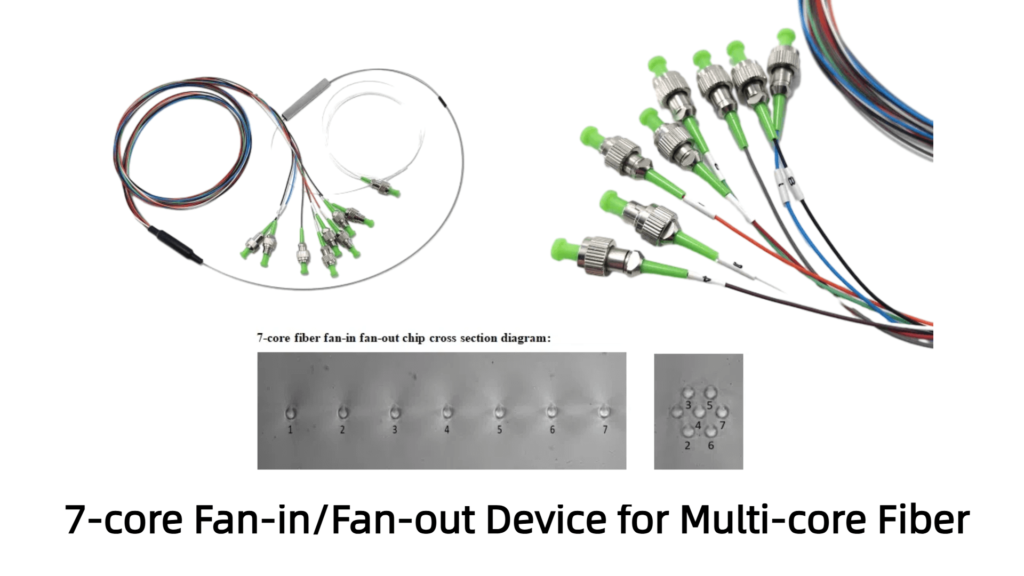
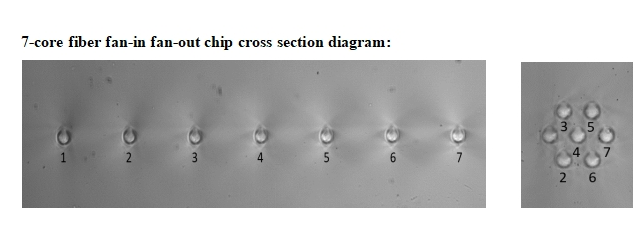
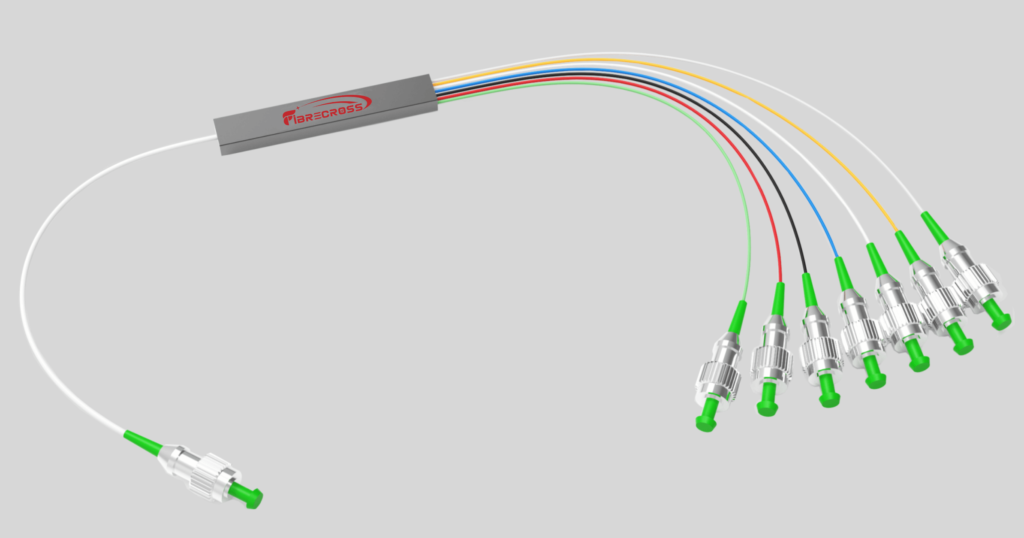
7-core Fan-in/Fan-out Device for Multi-core Fiber
In the ever-evolving landscape of optical communication, the demand for higher bandwidth and more efficient data transmission continues to grow. Multi-core fibers (MCFs) have emerged as a promising solution to meet these demands by incorporating multiple cores within a single fiber cladding. This allows for parallel data transmission, significantly increasing the capacity compared to traditional single-core fibers.
However, to fully harness the potential of MCFs, specialized components are required to interface with the individual cores. This is where fan-in/fan-out devices come into play. These devices act as crucial intermediaries, enabling the connection between individual fibers and the multiple cores of an MCF.
In this blog post, we will explore the 7-core fan-in/fan-out device, a key enabler for utilizing 7-core multi-core fibers in practical optical systems. We will delve into its design, technical specifications, and applications, providing insights for professionals in the field.
What is a Fan-in/Fan-out Device?
A fan-in/fan-out device is an optical component designed to manage the transition between individual fibers and the multiple cores of a multi-core fiber. Specifically, the “fan-out” aspect allows the separation of the MCF’s cores into individual fibers, while the “fan-in” aspect combines individual fibers into the cores of the MCF.
This bidirectional functionality is essential for integrating MCFs into existing optical networks, as it enables the use of standard single-core fiber components and systems with MCF technology.
The 7-core fan-in/fan-out device is tailored for MCFs with seven cores, a common configuration that balances increased capacity with manageable complexity.
The 7-core Fan-in/Fan-out Device
The 7-core fan-in/fan-out device is engineered to provide efficient and low-loss coupling between seven individual fibers and the seven cores of an MCF. Its design typically involves precision alignment techniques to ensure that each core is accurately matched with its corresponding fiber.
One of the critical challenges in designing such a device is minimizing insertion loss and crosstalk. Insertion loss refers to the reduction in optical power as light passes through the device, while crosstalk is the unwanted coupling of light between different cores.
To address these challenges, advanced manufacturing processes and materials are employed. For instance, the device may utilize tapered fiber bundles or planar lightwave circuits (PLCs) to achieve the necessary coupling with high precision.
Additionally, the device is often designed to be compact and robust, making it suitable for deployment in various environments, from laboratory settings to field installations.
Technical Specifications
Key technical specifications of a typical 7-core fan-in/fan-out device include:
- Insertion Loss: Less than 1 dB per channel, ensuring minimal signal degradation.
- Crosstalk: Below -40 dB, maintaining signal integrity across cores.
- Return Loss: Greater than 50 dB, reducing back-reflections.
- Wavelength Range: Compatible with standard telecommunication wavelengths, such as 1310 nm and 1550 nm.
- Fiber Type: Supports single-mode fibers for long-distance, high-speed transmission.
- Connector Types: Available with various connectors, such as LC, SC, or MPO, for easy integration.
These specifications highlight the device’s capability to deliver high-performance connectivity for MCF-based systems.
The key benefits of the 7-core Fan-in/Fan-out Device for Multi-core Fiber:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Bandwidth | Enables simultaneous data transmission across seven cores, boosting network capacity and efficiency. |
| Space Efficiency | Reduces the number of cables needed, optimizing space in network installations. |
| Scalability | Allows flexible integration into existing systems and easy scalability as network demands grow. |
| Reduced Latency | Improves data flow efficiency, reducing delays in high-speed, real-time applications. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lowers material and installation costs by consolidating multiple fiber strands into a single device. |
Applications of the 7-core Fan-in/Fan-out Device
Data Centers
Data centers are the backbone of the modern digital economy, and they require high-density, high-capacity fiber optic networks. The 7-core Fan-in/Fan-out device offers a solution that ensures smooth data transmission between servers, storage systems, and networking equipment.Telecommunications
Telecommunications companies can leverage this device to expand their fiber optic networks, providing faster and more reliable services to their customers. With the ability to aggregate and distribute signals across multiple cores, it supports more efficient backbone and access networks.High-Performance Computing (HPC)
HPC applications demand low-latency, high-bandwidth connections to support data-intensive computations. The 7-core Fan-in/Fan-out device helps meet these needs by providing a reliable and scalable solution for interconnecting computational nodes.Cloud Computing
Cloud service providers rely on high-speed fiber optic networks to support their infrastructure. The 7-core Fan-in/Fan-out device facilitates the interconnection of various cloud data centers, enhancing communication between distributed systems and improving overall cloud performance.
Conclusion
The 7-core Fan-in/Fan-out device for multi-core fiber is an essential innovation that addresses the growing demands of modern fiber optic networks. By enhancing bandwidth, improving space efficiency, reducing latency, and offering scalability, this device plays a pivotal role in the development of high-performance, cost-effective network infrastructures. As industries continue to require faster, more reliable communication solutions, multi-core fiber technology, along with fan-in/fan-out devices, will be at the forefront of driving future innovations in the world of telecommunications and data transfer.
Businesses that integrate this technology into their network infrastructure can expect to experience improved connectivity, greater efficiency, and a competitive edge in the fast-evolving digital landscape.